Multi Floor View & Stacked Maps
Using Mappedin SDK for Android with your own map requires a Pro license. Try a demo map for free or refer to the Pricing page for more information.
Multi Floor View
Multi Floor View is a feature that displays all floors in a building stacked vertically below the active floor, allowing users to see the building's vertical structure and navigate between floors. The active floor is fully rendered while lower floors appear as semi-transparent footprints.
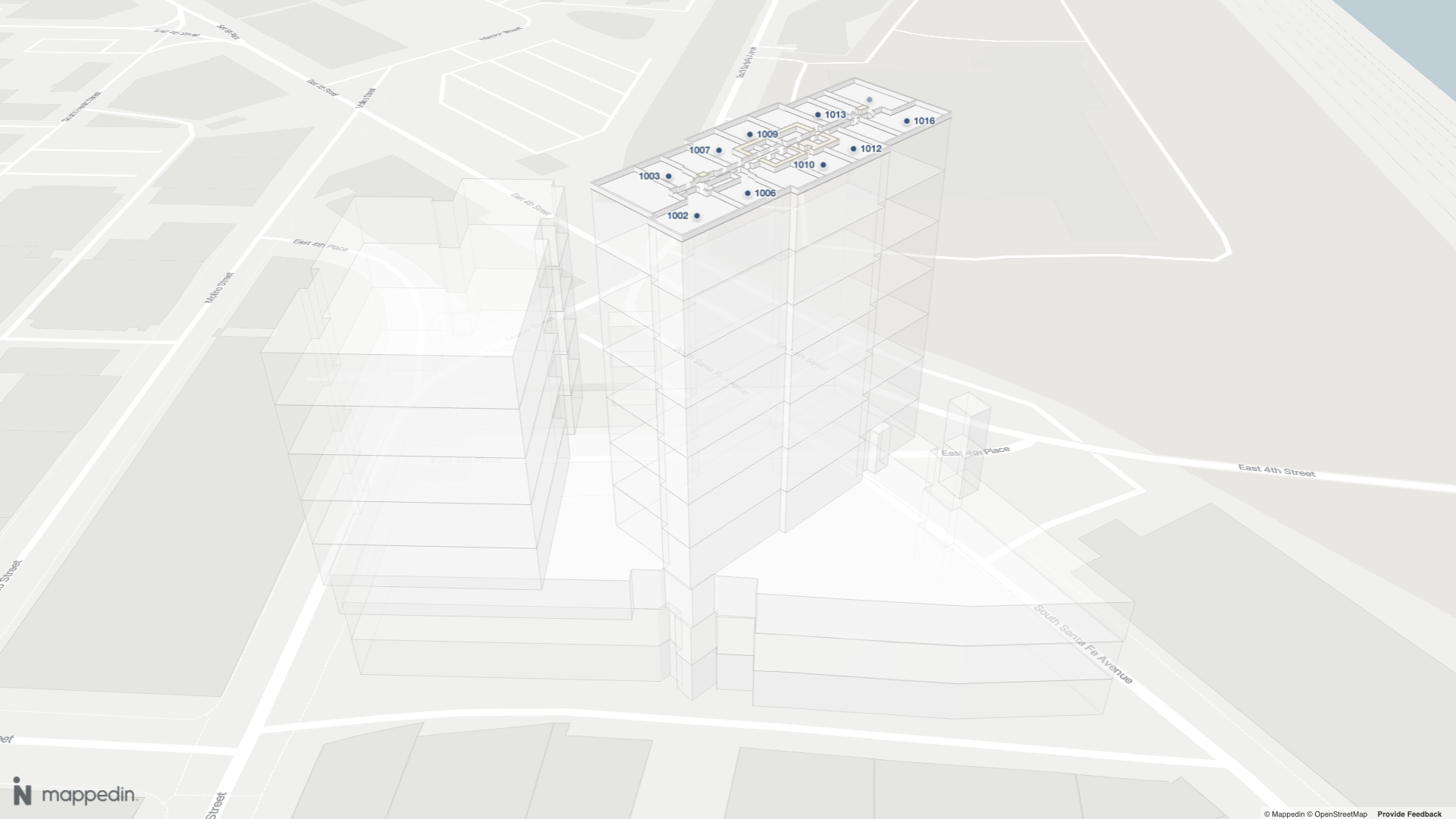
A complete example demonstrating Multi Floor View can be found in the Mappedin Android GitHub repo: MultiFloorViewDemoActivity.kt
Multi Floor View is enabled by default. It can be controlled using the Show3DMapOptions.multiFloorView option when initializing the map view as shown in the code sample below. In this example, the map view is initialized with the initialFloor set to m_952cd353abcb1a13, which is ID of the 10th floor of the building. Other Multi Floor View options are defined in MultiFloorViewOptions and include the ability to set the gap between floors as well as whether the camera should move when the active floor changes.
Code Sample
// Display the map with multi-floor view enabled.
val show3dMapOptions = Show3DMapOptions(
multiFloorView = MultiFloorViewOptions(
enabled = true,
floorGap = 10.0,
updateCameraElevationOnFloorChange = true,
)
)
mapView.show3dMap(show3dMapOptions) { r ->
r.onSuccess {
Log.d("MappedinDemo", "show3dMap success")
}
r.onFailure {
Log.e("MappedinDemo", "show3dMap error: $it")
}
}
It is possible to set multiple floors to be visible at once, which can be useful for overlaying data within the building, such as the locations of security cameras or other assets. This can be done by setting the visible property to true for each floor that should be shown, passing FloorUpdateState into MapView.updateState() as shown in the code sample below.
// Get all floors and find the ones needed.
mapView.mapData.getByType<Floor>(MapDataType.FLOOR) { result ->
result.onSuccess { floors ->
// Set the current floor to the one with elevation 9.
val floor9 = floors.find { it.elevation == 9.0 }
if (floor9 != null) {
mapView.setFloor(floor9.id) {
Log.d("MappedinDemo", "Set floor to elevation 9: ${floor9.name}")
}
}
// Show the 6th floor (elevation 6) as well.
val floor6 = floors.find { it.elevation == 6.0 }
if (floor6 != null) {
mapView.updateState(
floor6,
FloorUpdateState(
geometry = FloorUpdateState.Geometry(visible = true)
)
) {
Log.d("MappedinDemo", "Made floor with elevation 6 visible: ${floor6.name}")
}
}
}
result.onFailure {
Log.e("MappedinDemo", "Failed to get floors: $it")
}
}
When displaying multiple floors, by default content such as labels, markers, paths and images are only visible on the active floor. These can be displayed on additional visible floors by enabling them for the floor passing FloorUpdateState into MapView.updateState() as shown below.
mapView.updateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
visible = true,
altitude = 0.0,
geometry = FloorUpdateState.Geometry(visible = true),
images = FloorUpdateState.Images(visible = true),
labels = FloorUpdateState.Labels(enabled = true),
markers = FloorUpdateState.Markers(enabled = true),
paths = FloorUpdateState.Paths(visible = true)
)
) { result ->
result.onSuccess {
// Handle success
}
result.onFailure {
// Handle failure
}
}
Stacked Maps
Stacked Maps consist of individual layers that represent different floors of a multi-story building. These layers are conceptually or digitally stacked to create a complete view of the structure, allowing users to visualize, navigate, and interact with multiple floors in an integrated way.
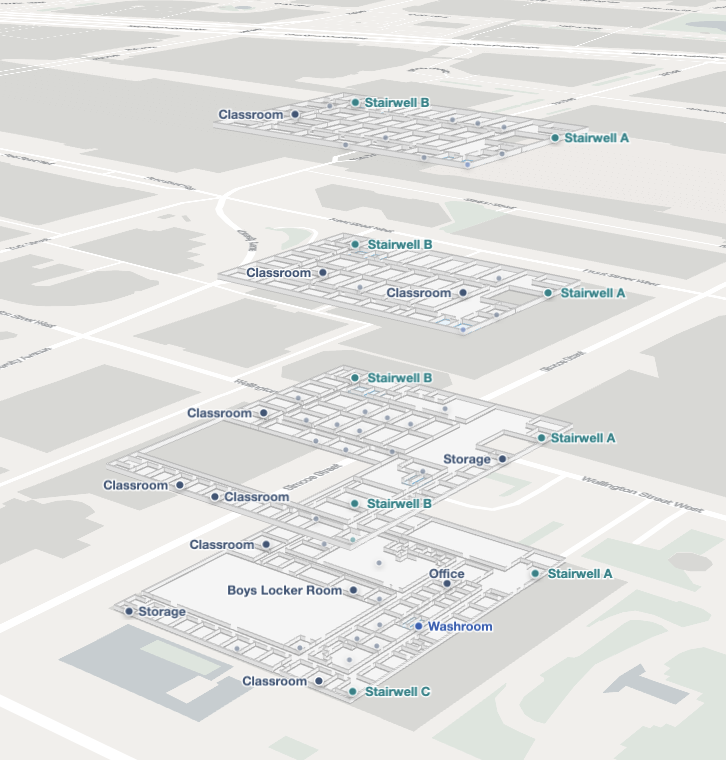
A complete example demonstrating Stacked Maps can be found in the Mappedin Android GitHub repo: StackedMapsDemoActivity.kt
Stacked Maps can be enabled by setting the visibility of floors that should appear in the stack to true and altering their altitude defined in FloorUpdateState, so that each floor is raised above the previous floor. There are two ways to modify the visibility and altitude of a floor:
- MapView.animateState() gradually moves the floor to the new altitude over a specified duration of time.
- MapView.updateState() instantly snaps the floor to the new altitude.
Alternative visualization methods can also be created by using variations of this technique. For example, an app may wish to only show the top and bottom floors of a building, or only show the floors that are currently accessible to the user by setting the visibility of the floors to true or false based on the app's requirements.
When displaying multiple floors, by default content such as labels, markers, paths and images are only visible on the active floor. These can be displayed on additional visible floors by enabling them for the floor passing FloorUpdateState into MapView.updateState() as shown below.
mapView.updateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
images = FloorUpdateState.Images(visible = true),
labels = FloorUpdateState.Labels(enabled = true),
markers = FloorUpdateState.Markers(enabled = true),
paths = FloorUpdateState.Paths(visible = true)
)
) { result ->
result.onSuccess {
// Handle success
}
result.onFailure {
// Handle failure
}
}
When using Stacked Maps with Dynamic Focus or Navigation, the MapView.manualFloorVisibility property should be set to true to ensure that the floors remain visible. Otherwise they could be hidden by the Dynamic Focus or Navigation features, which by default will hide all floors that are not the active floor.
Stacked Maps Utility Class
The following utility class can be used to expand and collapse the stacked maps view using the animateState or updateState methods.
package com.mappedin.demo
import com.mappedin.MapView
import com.mappedin.data.MapData
import com.mappedin.models.Floor
import com.mappedin.models.FloorUpdateState
import com.mappedin.models.MapDataType
/**
* Options for expanding floors in a stacked view.
*
* @param distanceBetweenFloors The vertical spacing between floors in meters. Default: 10
* @param animate Whether to animate the floor expansion. Default: true
* @param cameraPanMode The camera pan mode to use ("default" or "elevation"). Default: "elevation"
*/
data class ExpandOptions(
val distanceBetweenFloors: Double = 10.0,
val animate: Boolean = true,
val cameraPanMode: String = "elevation",
)
/**
* Options for collapsing floors back to their original positions.
*
* @param animate Whether to animate the floor collapse. Default: true
*/
data class CollapseOptions(
val animate: Boolean = true,
)
/**
* Utility object for managing stacked floor views.
*
* Provides functions to expand all floors vertically (stacked view) and collapse them back
* to a single floor view. This creates a 3D exploded view effect where all floors are visible
* at different altitudes.
*
* Example usage:
* ```kotlin
* // Expand floors with default options
* StackedMapsUtils.expandFloors(mapView)
*
* // Expand floors with custom gap
* StackedMapsUtils.expandFloors(mapView, ExpandOptions(distanceBetweenFloors = 20.0))
*
* // Collapse floors back
* StackedMapsUtils.collapseFloors(mapView)
* ```
*/
object StackedMapsUtils {
/**
* Expands all floors vertically to create a stacked view.
*
* Each floor is positioned at an altitude based on its elevation multiplied by the
* distance between floors. This creates a 3D exploded view where all floors are visible.
*
* @param mapView The MapView instance
* @param options Options controlling the expansion behavior
*/
fun expandFloors(
mapView: MapView,
options: ExpandOptions = ExpandOptions(),
) {
// Set camera pan mode to elevation for better navigation in stacked view
mapView.camera.setPanMode(options.cameraPanMode)
// Get the current floor ID to identify the active floor
mapView.currentFloor { currentFloorResult ->
val currentFloorId = currentFloorResult.getOrNull()?.id
// Get all floors
mapView.mapData.getByType<Floor>(MapDataType.FLOOR) { result ->
result.onSuccess { floors ->
floors.forEach { floor ->
val newAltitude = floor.elevation * options.distanceBetweenFloors
val isCurrentFloor = floor.id == currentFloorId
// First, make sure the floor is visible
mapView.getState(floor) { stateResult ->
stateResult.onSuccess { currentState ->
if (currentState != null &&
(!currentState.visible || !currentState.geometry.visible)
) {
// Make the floor visible first with 0 opacity if not current
mapView.updateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
visible = true,
altitude = 0.0,
geometry =
FloorUpdateState.Geometry(
visible = true,
opacity = if (isCurrentFloor) 1.0 else 0.0,
),
),
)
}
// Then animate or update to the new altitude
if (options.animate) {
mapView.animateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
altitude = newAltitude,
geometry =
FloorUpdateState.Geometry(
opacity = 1.0,
),
),
)
} else {
mapView.updateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
altitude = newAltitude,
visible = true,
geometry =
FloorUpdateState.Geometry(
visible = true,
opacity = 1.0,
),
),
)
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* Collapses all floors back to their original positions.
*
* Floors are returned to altitude 0, and only the current floor remains fully visible.
* Other floors are hidden to restore the standard single-floor view.
*
* @param mapView The MapView instance
* @param options Options controlling the collapse behavior
*/
fun collapseFloors(
mapView: MapView,
options: CollapseOptions = CollapseOptions(),
) {
// Reset camera pan mode to default
mapView.camera.setPanMode("default")
// Get the current floor ID to identify the active floor
mapView.currentFloor { currentFloorResult ->
val currentFloorId = currentFloorResult.getOrNull()?.id
// Get all floors
mapView.mapData.getByType<Floor>(MapDataType.FLOOR) { result ->
result.onSuccess { floors ->
floors.forEach { floor ->
val isCurrentFloor = floor.id == currentFloorId
if (options.animate) {
// Animate to altitude 0 and fade out non-current floors
mapView.animateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
altitude = 0.0,
geometry =
FloorUpdateState.Geometry(
opacity = if (isCurrentFloor) 1.0 else 0.0,
),
),
)
// After animation, hide non-current floors
if (!isCurrentFloor) {
// Use a handler to delay hiding the floor
android.os.Handler(android.os.Looper.getMainLooper()).postDelayed({
mapView.updateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
visible = false,
altitude = 0.0,
geometry =
FloorUpdateState.Geometry(
visible = false,
opacity = 0.0,
),
),
)
}, 1000) // Default animation duration
}
} else {
mapView.updateState(
floor,
FloorUpdateState(
altitude = 0.0,
visible = isCurrentFloor,
geometry =
FloorUpdateState.Geometry(
visible = isCurrentFloor,
opacity = if (isCurrentFloor) 1.0 else 0.0,
),
),
)
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
A complete example demonstrating Stacked Maps can be found in the Mappedin Android GitHub repo: StackedMapsDemoActivity.kt