Render MVF v2 with deck.gl
Mappedin Venue Format (MVF) v2 is currently in an beta state while Mappedin perfects a new design. Breaking changes may occur and this page will be updated to reflect this.
A GeoJSON renderer is required to display MVF data. For a full breakdown of the Mappedin Venue Format v2 (MVFv2) bundle, read the MVF Data Model. This guide will demonstrate how to get started using deck.gl, a popular and highly performant WebGL2 renderer.
Project Setup
- Start a new vanilla Vite project using TypeScript.
yarn create vite mappedin-mvf-guide
From the setup menu, select Vanilla, then TypeScript.
cd mappedin-mvf-guide
- Install deck.gl and related packages.
yarn add @deck.gl/core @deck.gl/layers @types/geojson jszip @turf/buffer
Update main.ts, style.css
Open the project in your editor. In the src directory, create or update the main.ts file and replace the contents with the code block below. Create a utils.ts file in the src directory copy the code below into these files. The rest of this guide will break down and explain the code.
import { Color, Deck } from '@deck.gl/core/typed';
import { GeoJsonLayer } from '@deck.gl/layers/typed';
import { Feature } from 'geojson';
import JSZip from 'jszip';
import './style.css';
import { downloadAndProcessVenue, getAccessToken, loadFileFromZip } from './utils';
//The Mappedin Map ID to load.
const MAP_ID = '64ef49e662fd90fe020bee61';
// See Trial API key Terms and Conditions
// https://developer.mappedin.com/docs/demo-keys-and-maps
const MAPPEDIN_KEY = 'mik_yeBk0Vf0nNJtpesfu560e07e5';
const MAPPEDIN_SECRET = 'mis_2g9ST8ZcSFb5R9fPnsvYhrX3RyRwPtDGbMGweCYKEq385431022';
const ELEVATION = 0; // The floor elevation to be displayed.
// Initialize the visualization with the GoeJSON files in the MVFv2 zip.
async function initVisualization(zip: JSZip) {
// Load the essential MVF data files from zip
const manifestData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, 'manifest.geojson');
const styles = await loadFileFromZip(zip, 'styles.json');
const floorData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, 'floor.geojson');
// Extract the features array from the FeatureCollection
const mapData = floorData.features.map(feature => feature.properties);
// Get the current map for the set elevation
const floorId = mapData.find(f => f.elevation === ELEVATION).id;
// Get geometry data by floor ID
const spaceData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, `space/${floorId}.geojson`);
const obstructionData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, `obstruction/${floorId}.geojson`);
function hexToRGB(hex: string): Color {
return hex.match(/[0-9a-f]{2}/g)!.map(x => parseInt(x, 16)) as Color;
}
// Space data contains traversable areas such as rooms and hallways
const roomStyles = styles['Rooms'];
const roomLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'room-layer',
data: spaceData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
roomStyles.polygons.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getFillColor: hexToRGB(roomStyles.color),
stroked: false,
});
const hallwayStyles = styles['Hallways'];
const hallwayLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'hallway-layer',
data: spaceData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
hallwayStyles.polygons.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getFillColor: hexToRGB(hallwayStyles.color),
stroked: false,
});
const wallStyles = styles['Walls'];
const wallLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'wall-layer',
data: obstructionData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
wallStyles.lineStrings.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getLineColor: hexToRGB(wallStyles.color),
getLineWidth: wallStyles.width,
stroked: false,
});
const exteriorWallStyles = styles['ExteriorWalls'];
const exteriorWallLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'exterior-wall-layer',
data: obstructionData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
exteriorWallStyles.lineStrings.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getLineColor: hexToRGB(exteriorWallStyles.color),
getLineWidth: exteriorWallStyles.width,
stroked: false,
});
const deskStyles = styles['Desks'];
const deskLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'desk-layer',
data: obstructionData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
deskStyles.polygons.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getFillColor: hexToRGB(deskStyles.color),
stroked: false,
});
new Deck({
initialViewState: {
longitude: manifestData.features[0].geometry.coordinates[0],
latitude: manifestData.features[0].geometry.coordinates[1],
zoom: 19,
},
controller: true,
layers: [roomLayer, hallwayLayer, deskLayer, wallLayer, exteriorWallLayer],
});
}
// Execute everything
getAccessToken(MAPPEDIN_KEY, MAPPEDIN_SECRET)
.then(async token => {
const zip = await downloadAndProcessVenue(token, MAP_ID);
// Initialize visualization with the zip contents.
await initVisualization(zip);
})
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));
import JSZip from 'jszip';
interface TokenResponse {
access_token: string;
expires_in: number;
}
interface VenueResponse {
url: string;
updated_at: string;
}
// Use the MappedIn API key & secret to get an access token.
export async function getAccessToken(key: String, secret: String): Promise<string> {
// See Trial API key Terms and Conditions
// https://developer.mappedin.com/docs/demo-keys-and-maps
const response = await fetch('https://app.mappedin.com/api/v1/api-key/token', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
key: key,
secret: secret,
}),
});
const data: TokenResponse = await response.json();
return data.access_token;
}
// Load a file from a zip archive.
export async function loadFileFromZip(zip: JSZip, path: string) {
const file = zip.file(path);
if (!file) throw new Error(`File not found in zip: ${path}`);
const content = await file.async('text');
return JSON.parse(content);
}
// Download the MVFv2 zip file from the MappedIn API and process it.
export async function downloadAndProcessVenue(accessToken: string, mapId: string): Promise<JSZip> {
const venueResponse = await fetch(`https://app.mappedin.com/api/venue/${mapId}/mvf`, {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
});
const venueData: VenueResponse = await venueResponse.json();
// Download the zip file
const zipResponse = await fetch(venueData.url);
const zipBuffer = await zipResponse.arrayBuffer();
// Process zip contents in memory
const zip = new JSZip();
await zip.loadAsync(zipBuffer);
return zip;
}
export function hexToRGB(hex: string): string {
const rgb = hex.match(/[0-9a-f]{2}/g)!.map(x => parseInt(x, 16));
return `rgba(${rgb[0]}, ${rgb[1]}, ${rgb[2]}, 0.95)`;
}
body {
background-color: darkseagreen;
}
Get an Access Token
The Mappedin API requires an access token to download the MVF bundle. This guide will use the Demo API key to get an access token from the API Key REST endpoint.
// Use the MappedIn API key & secret to get an access token.
export async function getAccessToken(key: String, secret: String): Promise<string> {
// See Trial API key Terms and Conditions
// https://developer.mappedin.com/docs/demo-keys-and-maps
const response = await fetch('https://app.mappedin.com/api/v1/api-key/token', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
key: key,
secret: secret,
}),
});
const data: TokenResponse = await response.json();
return data.access_token;
}
Download the MVF Bundle
The Get Venue MVF endpoint is called with the venue/map ID. The response contains a URL to the MVFv2 bundle, which is downloaded, loaded into memory, and passed to the initVisualization function.
// Download the MVFv2 zip file from the MappedIn API and process it.
export async function downloadAndProcessVenue(accessToken: string, mapId: string): Promise<JSZip> {
const venueResponse = await fetch(`https://app.mappedin.com/api/venue/${mapId}/mvf`, {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
});
const venueData: VenueResponse = await venueResponse.json();
// Download the zip file
const zipResponse = await fetch(venueData.url);
const zipBuffer = await zipResponse.arrayBuffer();
// Process zip contents in memory
const zip = new JSZip();
await zip.loadAsync(zipBuffer);
return zip;
}
Loading the Data
The GeoJSON data for an MVF is split into multiple parts, often separated by floor ID. The structure of this bundle is explained in the MVF v2 Data Model. the loadFileFromZip function is used to load the GeoJSON files from the zip archive and return them as JSON objects.
// Load a file from a zip archive.
export async function loadFileFromZip(zip: JSZip, path: string) {
const file = zip.file(path);
if (!file) throw new Error(`File not found in zip: ${path}`);
const content = await file.async('text');
return JSON.parse(content);
}
For a basic 2D or 3D rendering, the following datasets are needed:
Some data - like Space and Obstruction - is divided by floor ID. Using the desired elevation, the floor ID can be pulled from the Floor GeoJSON file. Then, in the fetch specify which floor ID file to load.
// Load the essential MVF data files from zip
const manifestData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, 'manifest.geojson');
const styles = await loadFileFromZip(zip, 'styles.json');
const floorData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, 'floor.geojson');
// Extract the features array from the FeatureCollection
const mapData = floorData.features.map(feature => feature.properties);
// Get the current map for the set elevation
const floorId = mapData.find(f => f.elevation === ELEVATION).id;
// Get geometry data by floor ID
const spaceData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, `space/${floorId}.geojson`);
const obstructionData = await loadFileFromZip(zip, `obstruction/${floorId}.geojson`);
Rendering the Geometry
The Space and Obstruction datasets contain the geometry of the map, but they don't contain any properties which specify how they should be rendered. The MVF comes with a Styles JSON file for this purpose.
Open styles.json in an editor to preview some of the style sets available. The key names are not guaranteed, but are generally English descriptors such as Rooms or Walls. Each style has a list of either polygons or lineStrings which belong to it.
Create a new DeckGL GeoJsonLayer for rooms. To select only the rooms from the Space GeoJSON, filter the dataset by polygons included in the Rooms Styles. Since these are polygons, apply the color to getFillColor in DeckGL.
const roomStyles = styles['Rooms'];
const roomLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'room-layer',
data: spaceData.features.filter((f: Feature) => roomStyles.polygons.includes(f.properties!.id)),
getFillColor: hexToRGB(roomStyles.color),
stroked: false,
});
Similarly, the same process is done for Hallways.
const hallwayStyles = styles['Hallways'];
const hallwayLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'hallway-layer',
data: spaceData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
hallwayStyles.polygons.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getFillColor: hexToRGB(hallwayStyles.color),
stroked: false,
});
There are 3 main Styles for Obstruction GeoJSON data, Walls, ExteriorWalls, and Desks. Follow the same process, however, Walls and ExteriorWalls are lineStrings. As such, set getLineColor and getLineWidth in the GeoJsonLayer.
const wallStyles = styles['Walls'];
const wallLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'wall-layer',
data: obstructionData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
wallStyles.lineStrings.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getLineColor: hexToRGB(wallStyles.color),
getLineWidth: wallStyles.width,
stroked: false,
});
const exteriorWallStyles = styles['ExteriorWalls'];
const exteriorWallLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'exterior-wall-layer',
data: obstructionData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
exteriorWallStyles.lineStrings.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getLineColor: hexToRGB(exteriorWallStyles.color),
getLineWidth: exteriorWallStyles.width,
stroked: false,
});
const deskStyles = styles['Desks'];
const deskLayer = new GeoJsonLayer({
id: 'desk-layer',
data: obstructionData.features.filter((f: Feature) =>
deskStyles.polygons.includes(f.properties!.id)
),
getFillColor: hexToRGB(deskStyles.color),
stroked: false,
});
Finally, create the Deck object and attach the layers. The Manifest GeoJSON contains the center coordinate of the map, which is used to set the initialViewState. List the geometry layers in the order that they stack vertically. For example, the Desks and Walls should be a layer above the Rooms and Hallways.
new Deck({
initialViewState: {
longitude: manifestData.features[0].geometry.coordinates[0],
latitude: manifestData.features[0].geometry.coordinates[1],
zoom: 18,
},
controller: true,
layers: [roomLayer, hallwayLayer, deskLayer, wallLayer, exteriorWallLayer],
});
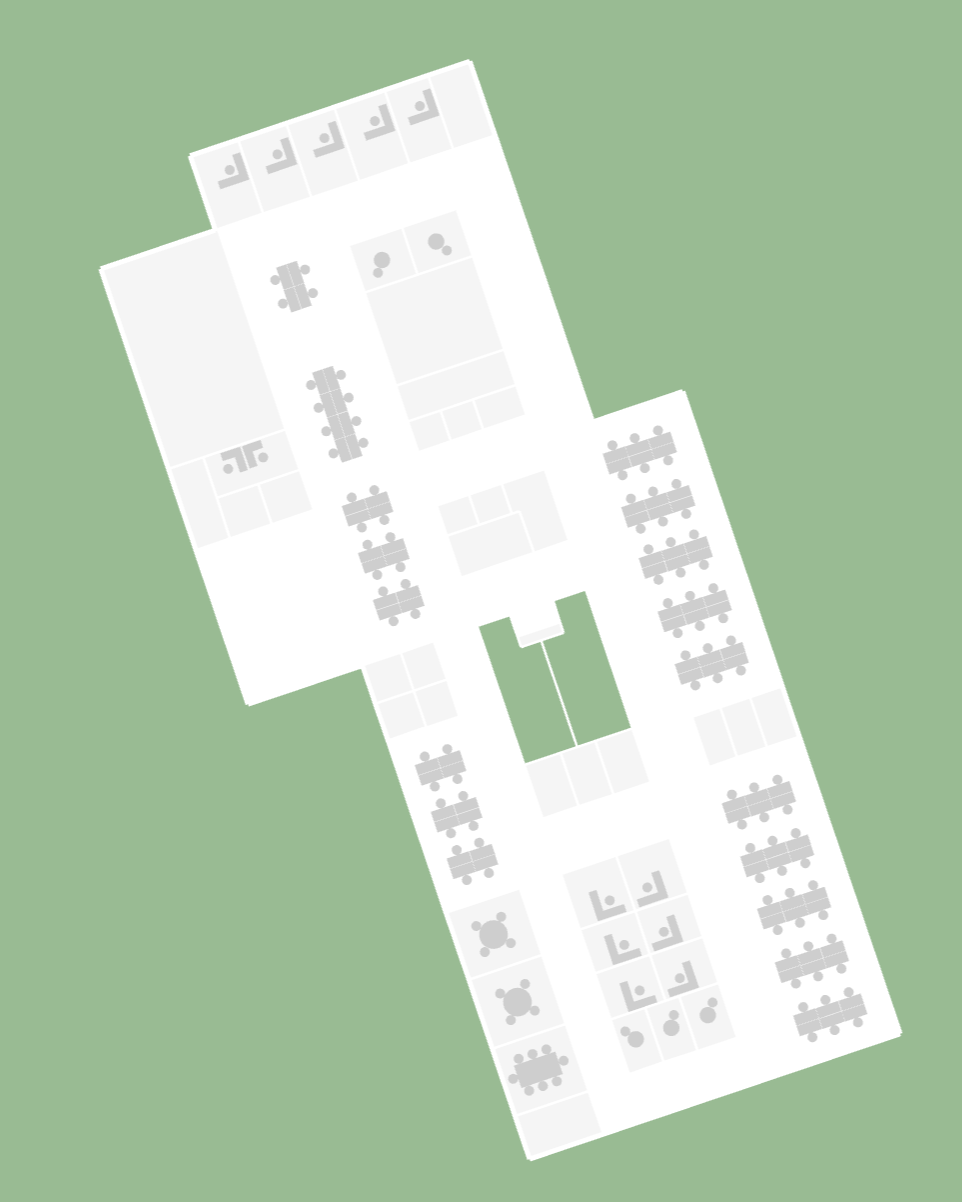
End Result
The end result should be a 2D render of the MVF v2 in DeckGL. The following CodeSandbox implements this guide with the Dev Office Demo Map.